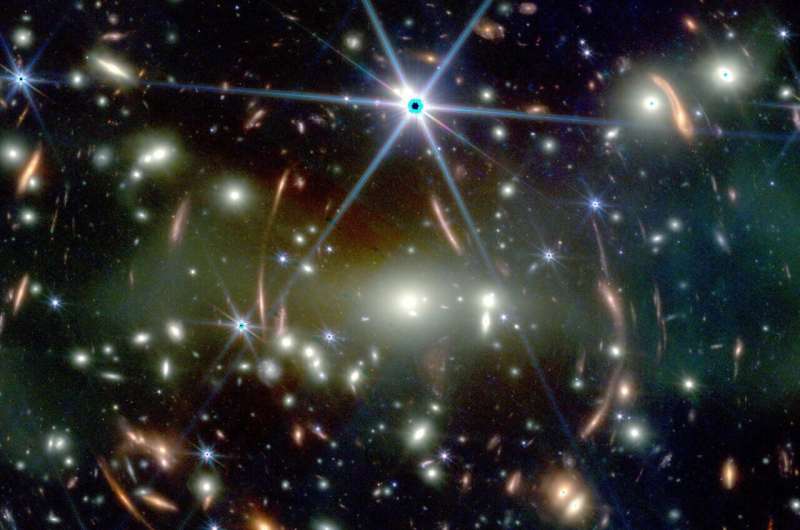
This JWST picture reveals galaxy cluster SMACS J0723.3−7327 with numerous lensed background galaxies. The white bar on the backside corresponds to 50 arcseconds, roughly the utmost dimension of Jupiter noticed from Earth. Credit score: NASA, ESA, ASC and STScI
Utilizing the primary scientific picture launched by the James Webb Area Telescope (JWST) this month, a world workforce of scientists with vital enter from the Technical College of Munich (TUM) have constructed an improved mannequin for the mass distribution of galaxy cluster SMACS J0723.3−7327. Performing as a so-called gravitational lens, the foreground galaxy cluster each produces a number of photographs of background galaxies and magnifies these photographs. One household of those a number of photographs belongs to a galaxy, which the mannequin predicts at a distance of about 13 Gyrs, that’s, whose mild has traveled about 13 billion years earlier than reaching the telescope.
The primary scientific picture launched by the James Webb Area Telescope (JWST) was of a gravitational lens, particularly the galaxy cluster SMACS J0723.3−7327. Gravitational lenses, particularly galaxy clusters, amplify the sunshine from background galaxies and produce a number of photographs of them. Previous to JWST, 19 a number of photographs of six background sources had been identified in SMACS J0723.3−7327. JWST information has now revealed a further 27 a number of photographs from ten different lensed sources.
“On this first step in the direction of the trail opened by JWST, we used current information from this model new telescope to mannequin the lensing impact of SMACS0723 with nice precision”, factors out Gabriel Bartosch Caminha, postdoctoral fellow at TUM, the Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics (MPA) and the German Heart for Cosmological Lenses (GCCL). The collaboration first used information from the Hubble Area Telescope (HST) and Multi-Unit Spectroscopic Explorer (MUSE) to construct a “pre-JWST” lens mannequin, then refined it with close to imaging. newly obtainable JWST infrared. “The JWST imagery is totally gorgeous and delightful, displaying many extra multi-lens background sources, which allowed us to considerably refine our lens mass mannequin,” he provides.
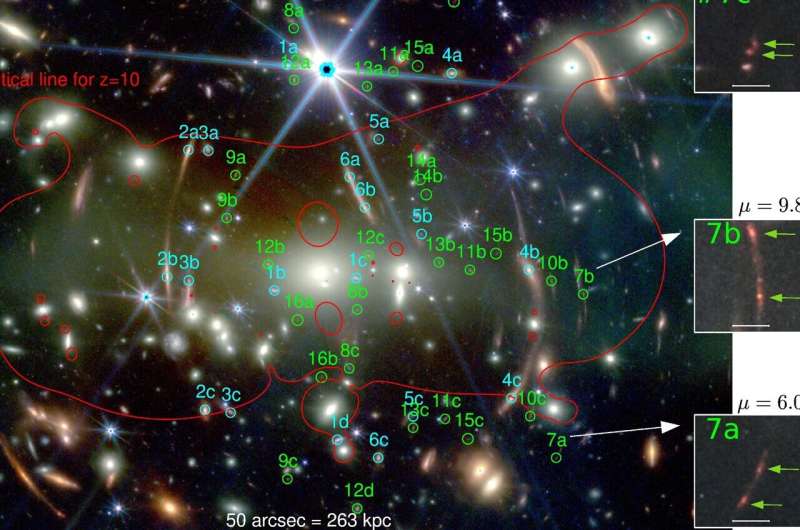
On this picture, the varied multi-lens background galaxies are numbered, with cyan colours indicating beforehand identified multi-image methods and inexperienced colours indicating new multi-lens sources. The insets present magnified photographs of a really distant galaxy with substructure indicated by the inexperienced arrows. Credit score: NASA, ESA, CSA and STScI (annotations by MPA)
One of the vital correct fashions obtainable
Many of those new lensed sources do not but have distance estimates, and scientists have used their mass mannequin to foretell how far-off these lensed galaxies are most certainly to be. Considered one of them turned out to be most likely on the astonishing distance of 13 Gyrs (redshift >7.5), i.e. its mild was emitted throughout the early phases of the universe. This galaxy is lensed in three frames and its brightness is magnified by an element of μ≈20 in whole.
Nevertheless, to check these primordial objects, it’s basic to precisely describe the lensing impact of the foreground galaxy cluster. “Our correct mass mannequin kinds the idea for JWST information mining,” says Sherry Suyu, Professor of Observational Cosmology at TUM, Max Planck Analysis Group Chief at MPA and Visiting Scholar on the Institute of Astronomy and Science. Astrophysics Academia Sinica. “The spectacular JWST photographs present all kinds of strong-lens galaxies, which might be studied intimately with our exact mannequin.”
The brand new main cluster mass distribution mannequin is ready to reproduce the positions of all a number of photographs with excessive accuracy, making it one of the correct fashions obtainable. For follow-up research of those sources, lens fashions, together with magnification maps and redshifts (i.e. distances) estimated from the mannequin are made public. “We’re very enthusiastic about this,” provides Suyu. “We look ahead to future JWST observations of different robust lensed galaxy clusters. These will enable us not solely to raised constrain the mass distributions of galaxy clusters, but additionally to check redshift galaxies raised.”
How the James Webb Area Telescope Lets Us See the Universe’s First Galaxies
GB Caminha et al, First JWST observations of a gravitational lens: mass mannequin of recent a number of photographs with near-infrared observations of SMACS ~ J0723.3−7327. arXiv:2207.07567v1 [astro-ph.GA]arxiv.org/abs/2207.07567
Offered by the Technical College of Munich
Quote: Improved mannequin for the mass distribution of the galaxy cluster SMACS J0723.3−7327 primarily based on the Webb Telescope picture (2022, July 28) retrieved July 29, 2022 from https://phys.org/information/ 2022-07-mass-galaxy-cluster-smacs-j072337327.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from honest use for functions of personal research or analysis, no half could also be reproduced with out written permission. The content material is offered for data solely.
#Improved #mannequin #mass #distribution #galaxy #cluster #SMACS #J0723.37327 #primarily based #Webb #Telescope #picture



